Load Data Into Cosmos DB with ADF
In this lab, you will populate an Azure Cosmos DB container from an existing set of data using tools built in to Azure. After importing, you will use the Azure portal to view your imported data.
If you have not already completed setup for the lab content see the instructions for Account Setup before starting this lab. This will create an Azure Cosmos DB database and container that you will use throughout the lab. You will also use an Azure Data Factory (ADF) resource to import existing data into your container.
Create Azure Cosmos DB Database and Container
You will now create a database and container within your Azure Cosmos DB account.
-
Navigate to the Azure Portal
-
On the left side of the portal, select the Resource groups link.
-
In the Resource groups blade, locate and select the cosmoslabs resource group.
-
In the cosmoslabs blade, select the Azure Cosmos DB account you recently created.
-
In the Azure Cosmos DB blade, locate and select the Overview link on the left side of the blade. At the top select the Add Container button.
-
In the Add Container popup, perform the following actions:
-
In the Database id field, select the Create new option and enter the value ImportDatabase.
-
Do not check the Provision database throughput option.
Provisioning throughput for a database allows you to share the throughput among all the containers that belong to that database. Within an Azure Cosmos DB database, you can have a set of containers which shares the throughput as well as containers, which have dedicated throughput.
-
In the Container Id field, enter the value FoodCollection.
-
In the Partition key field, enter the value
/foodGroup. -
In the Throughput field, enter the value
11000. Note: we will reduce this to 400 RU/s after the data has been imported -
Select the OK button.
-
-
Wait for the creation of the new database and container to finish before moving on with this lab.
Import Lab Data Into Container
You will use Azure Data Factory (ADF) to import the JSON array stored in the nutrition.json file from Azure Blob Storage.
You do not need to do Steps 1-4 in this section and can proceed to Step 4 by opening your Data Factory (named importNutritionData with a random number suffix)if you are completing the lab through Microsoft Hands-on Labs or ran the setup script, you can use the pre-created Data Factory within your resource group.
-
On the left side of the portal, select the Resource groups link.
To learn more about copying data to Cosmos DB with ADF, please read ADF’s documentation.

-
In the Resource groups blade, locate and select the cosmoslabs resource group.
-
If you see a Data Factory resource, you can skip to step 4, otherwise select Add to add a new resource
- Search for Data Factory and select it.
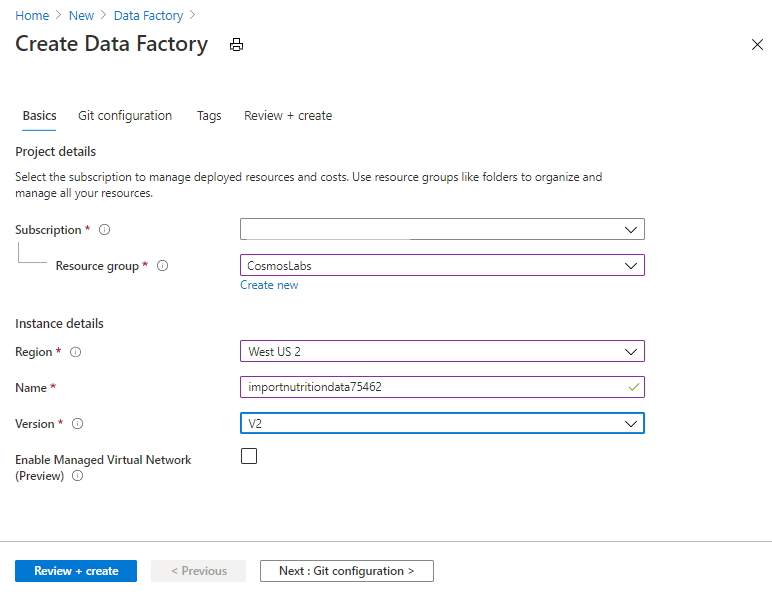
- Create a new Data Factory. You should name this data factory importnutritiondata with a unique number appended and select the relevant Azure subscription. You should ensure your existing cosmoslabs resource group is selected as well as a Version V2.
- Select East US as the region. Do not select Enable GIT (this may be checked by default).
-
Select Create.
-
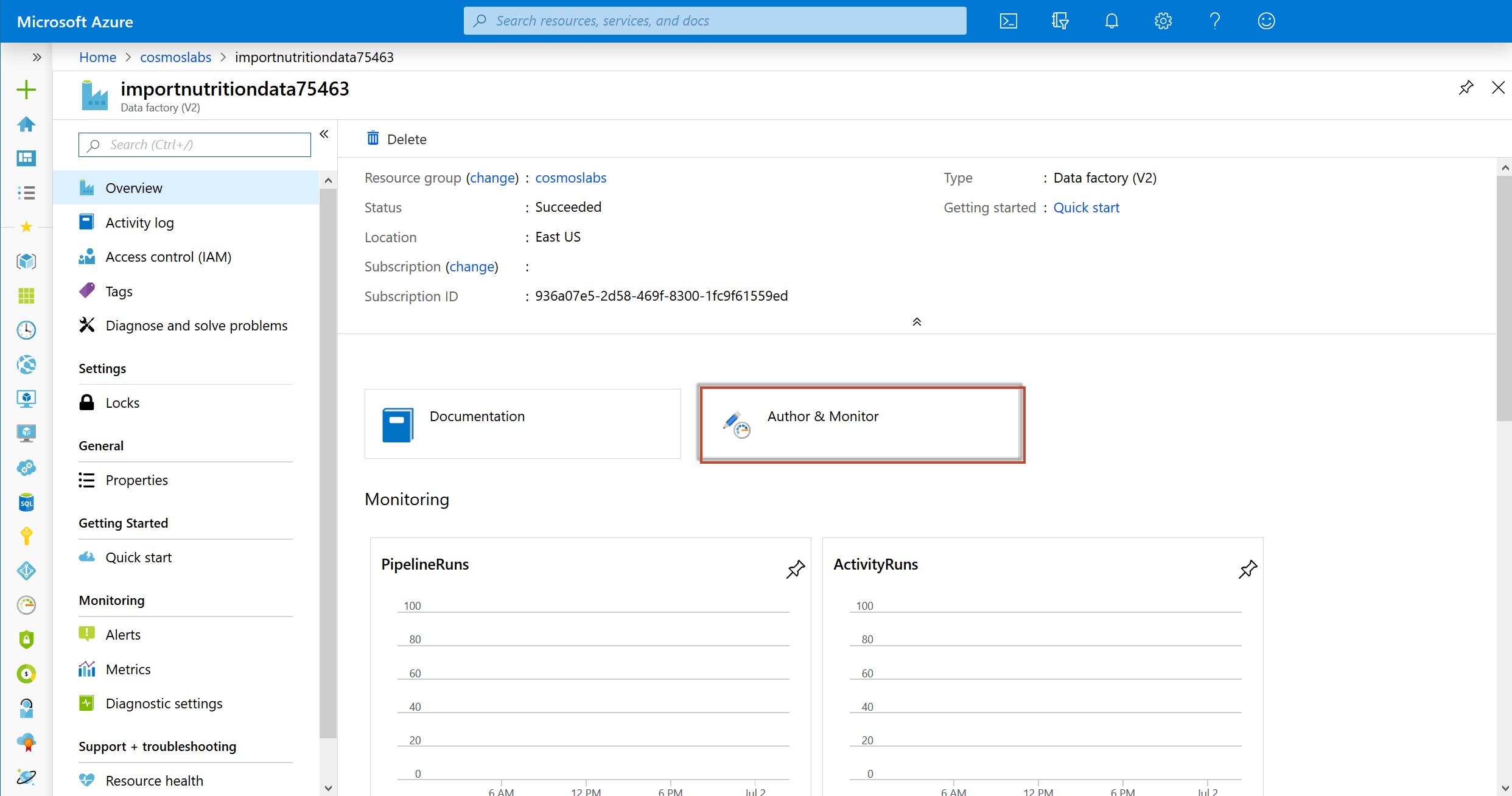
After creation, open your newly created Data Factory. Select Author & Monitor and you will launch ADF.
-
Select Copy Data.
- We will be using ADF for a one-time copy of data from a source JSON file on Azure Blob Storage to a database in Cosmos DB’s SQL API. ADF can also be used for more frequent data transfers from Cosmos DB to other data stores.

-
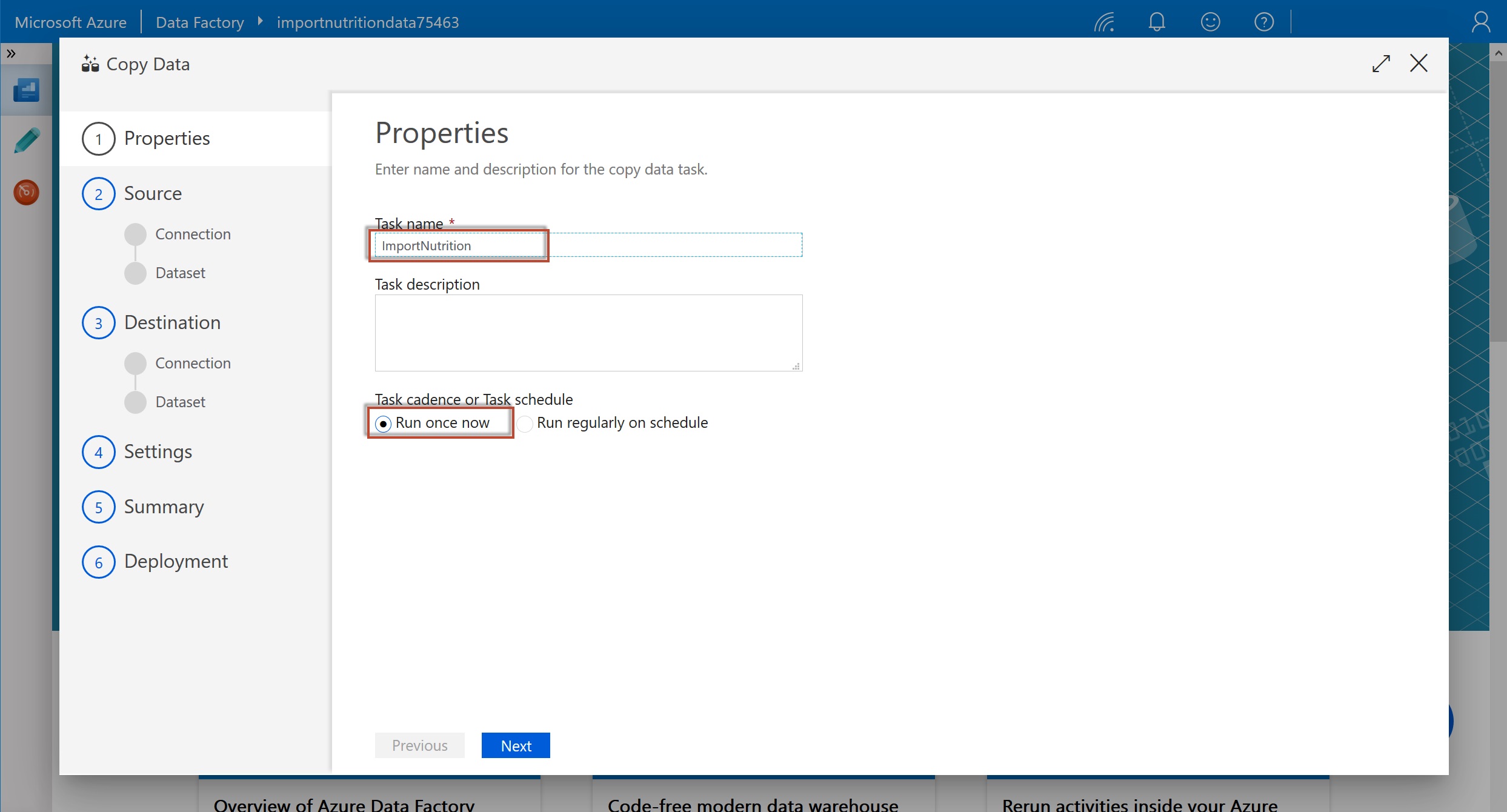
Edit basic properties for this data copy. You should name the task ImportNutrition and select to Run once now, then select Next
-
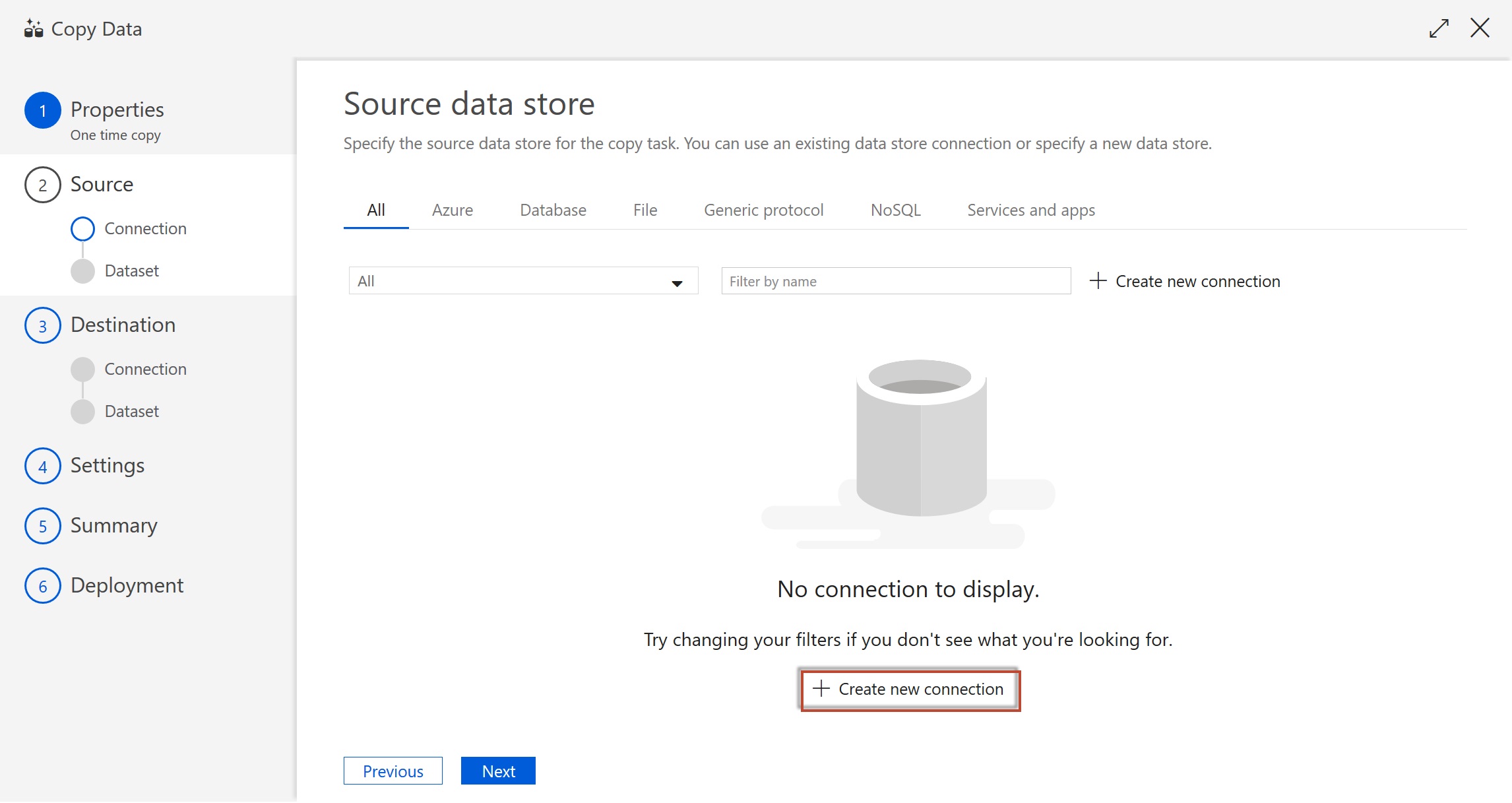
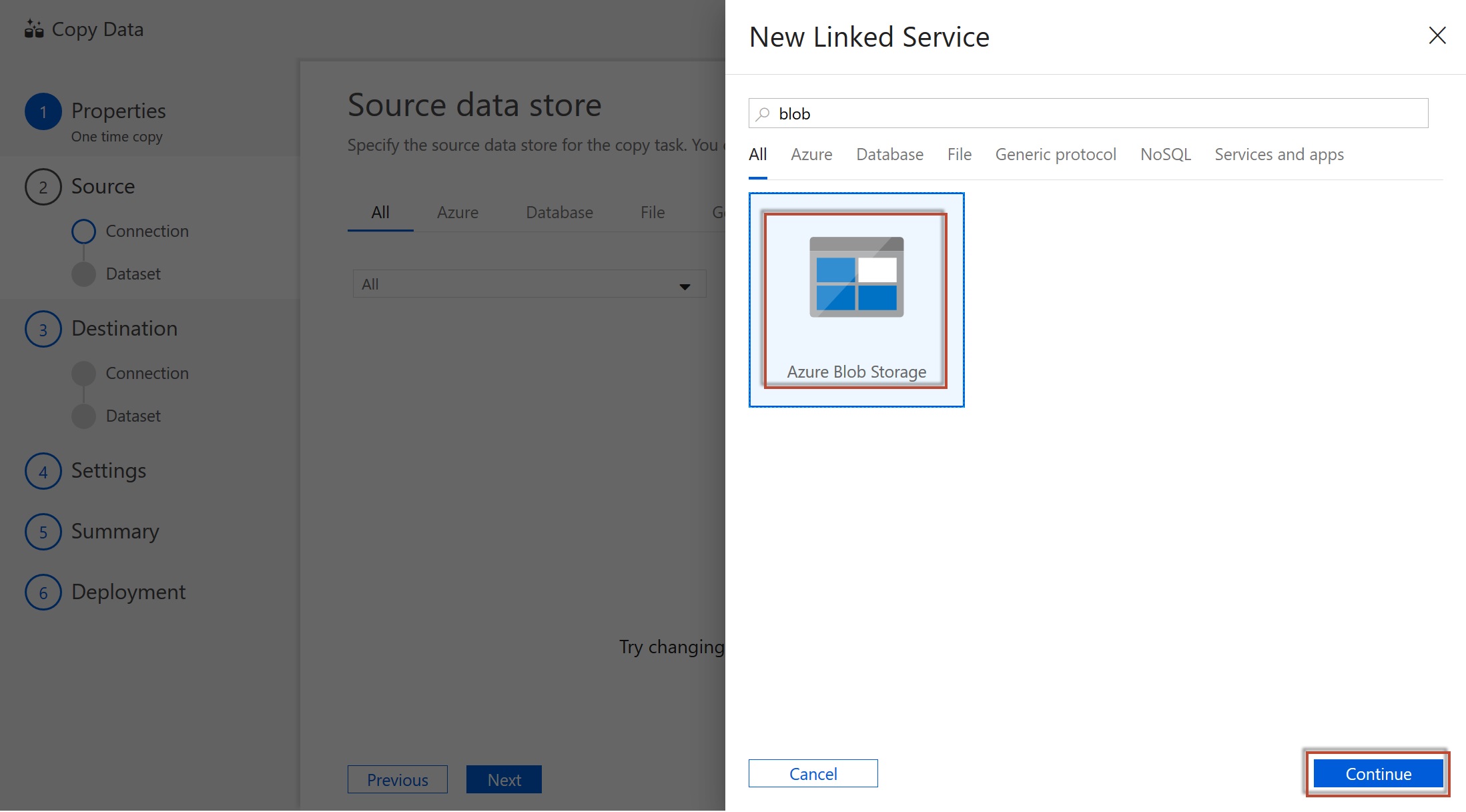
Create a new connection and select Azure Blob Storage. We will import data from a json file on Azure Blob Storage. In addition to Blob Storage, you can use ADF to migrate from a wide variety of sources. We will not cover migration from these sources in this tutorial.
-
Name the source NutritionJson and select SAS URI as the Authentication method. Please use the following SAS URI for read-only access to this Blob Storage container:
https://cosmoslabsstorageaccount.blob.core.windows.net/nutrition-data?si=container-list-read-policy&spr=https&sv=2021-06-08&sr=c&sig=jGrmrokYikbgbuW9we2am%2BwAq%2BC%2BxfZcPYswOeSQpAU%3D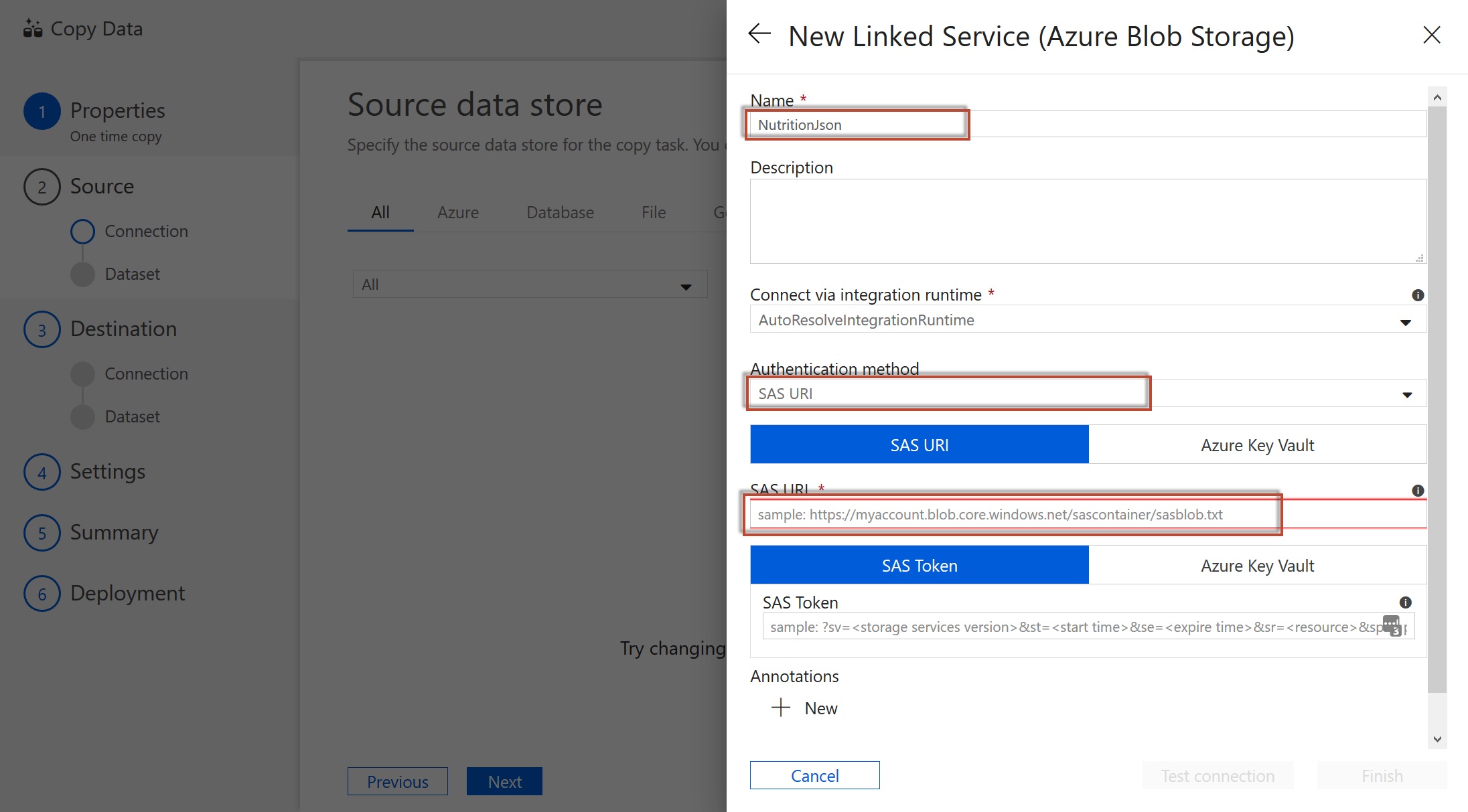
- Select Create
- Select Next
-
In the File or Folder textbox, enter the folder name as
nutirion-dataand then click on Browse to select the nutrition-data folder. Finally select NutritionData.json file.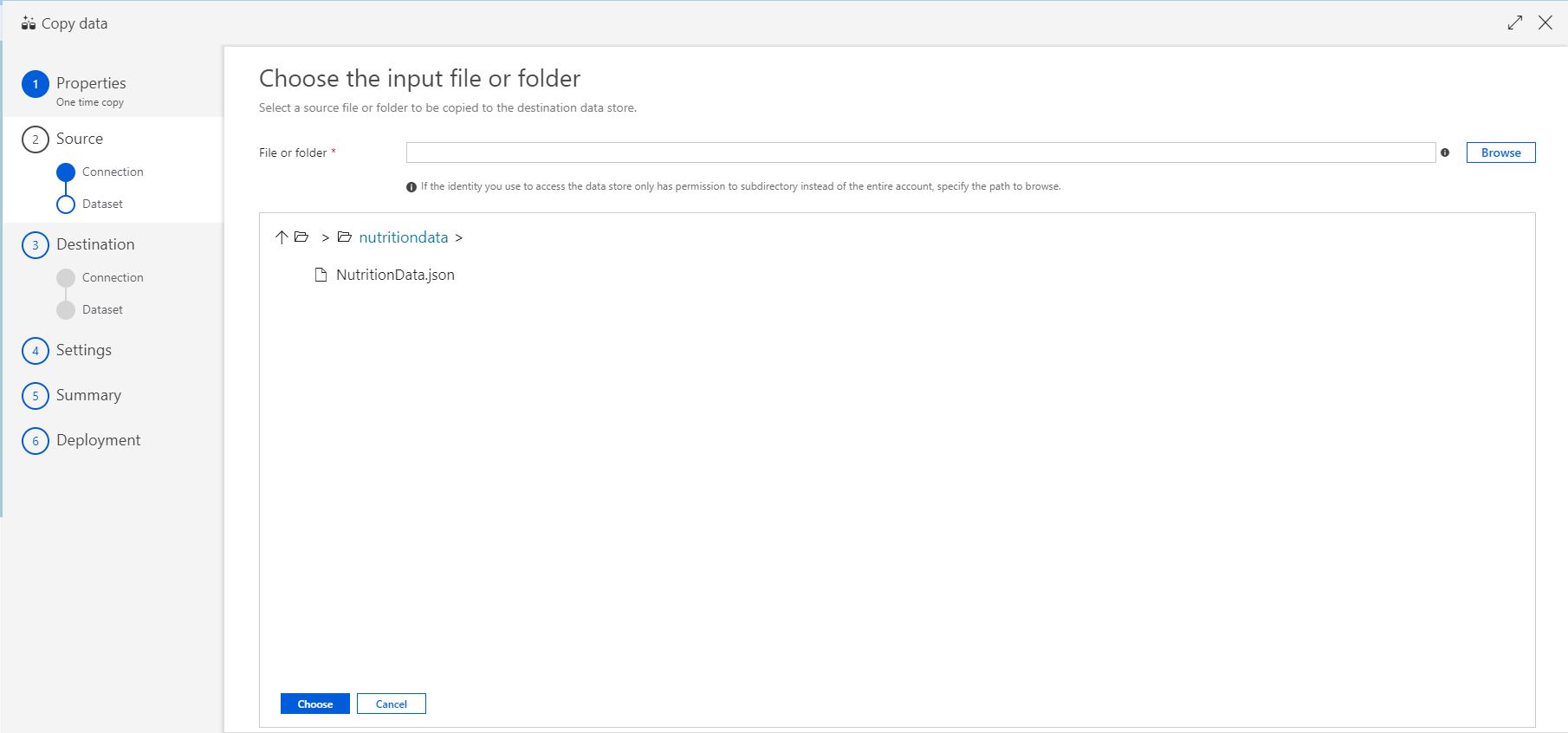
-
Un-check Copy file recursively or Binary Copy if they are checked. Also ensure that other fields are empty. Click Next
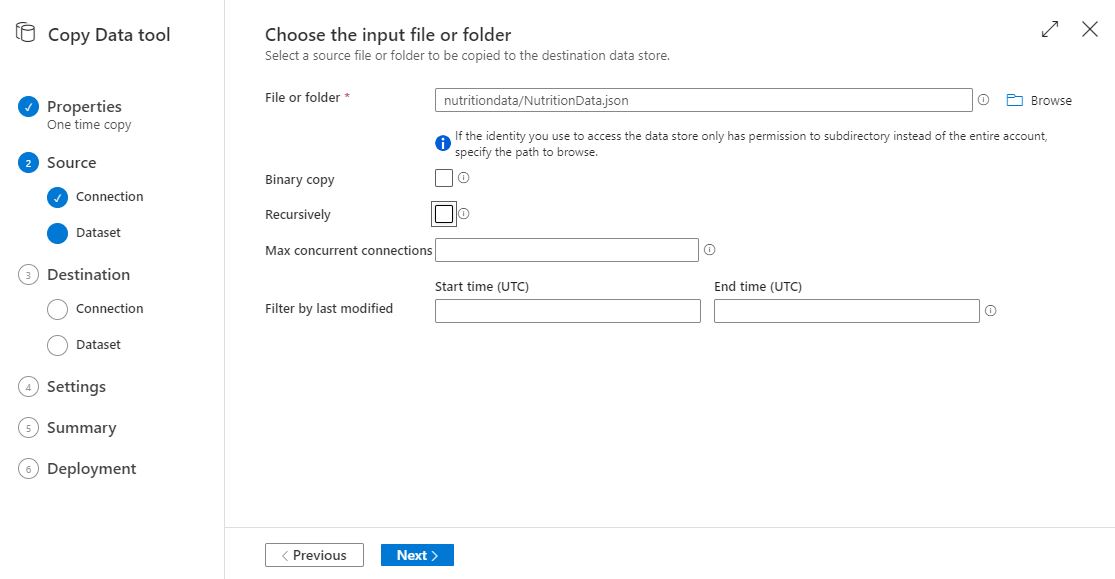
-
Select the file format as JSON format. Then select Next.
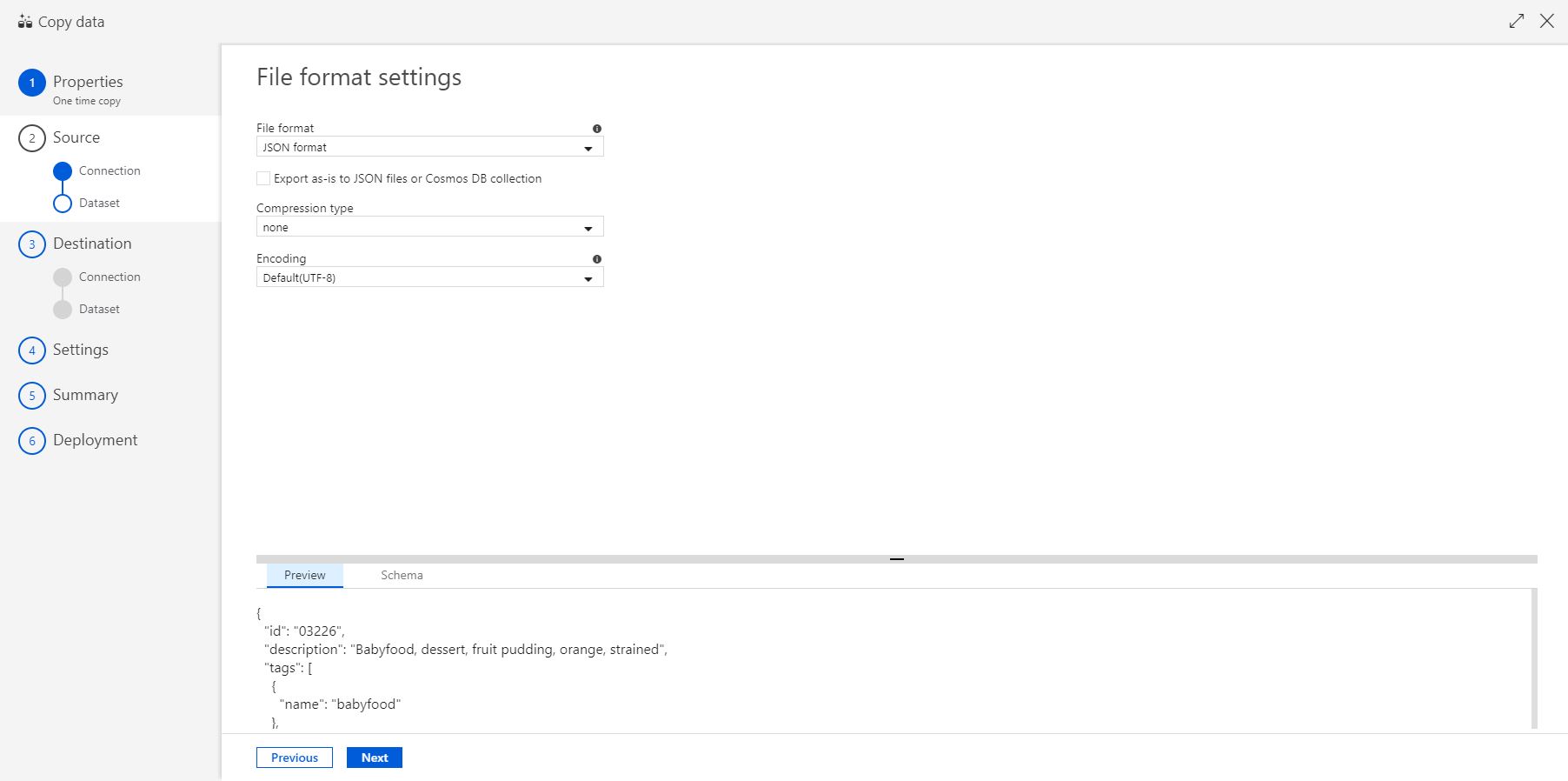
-
You have now successfully connected the Blob Storage container with the nutrition.json file as the source.
-
For the Destination data store add the Cosmos DB target data store by selecting Create new connection and selecting Azure Cosmos DB (SQL API).
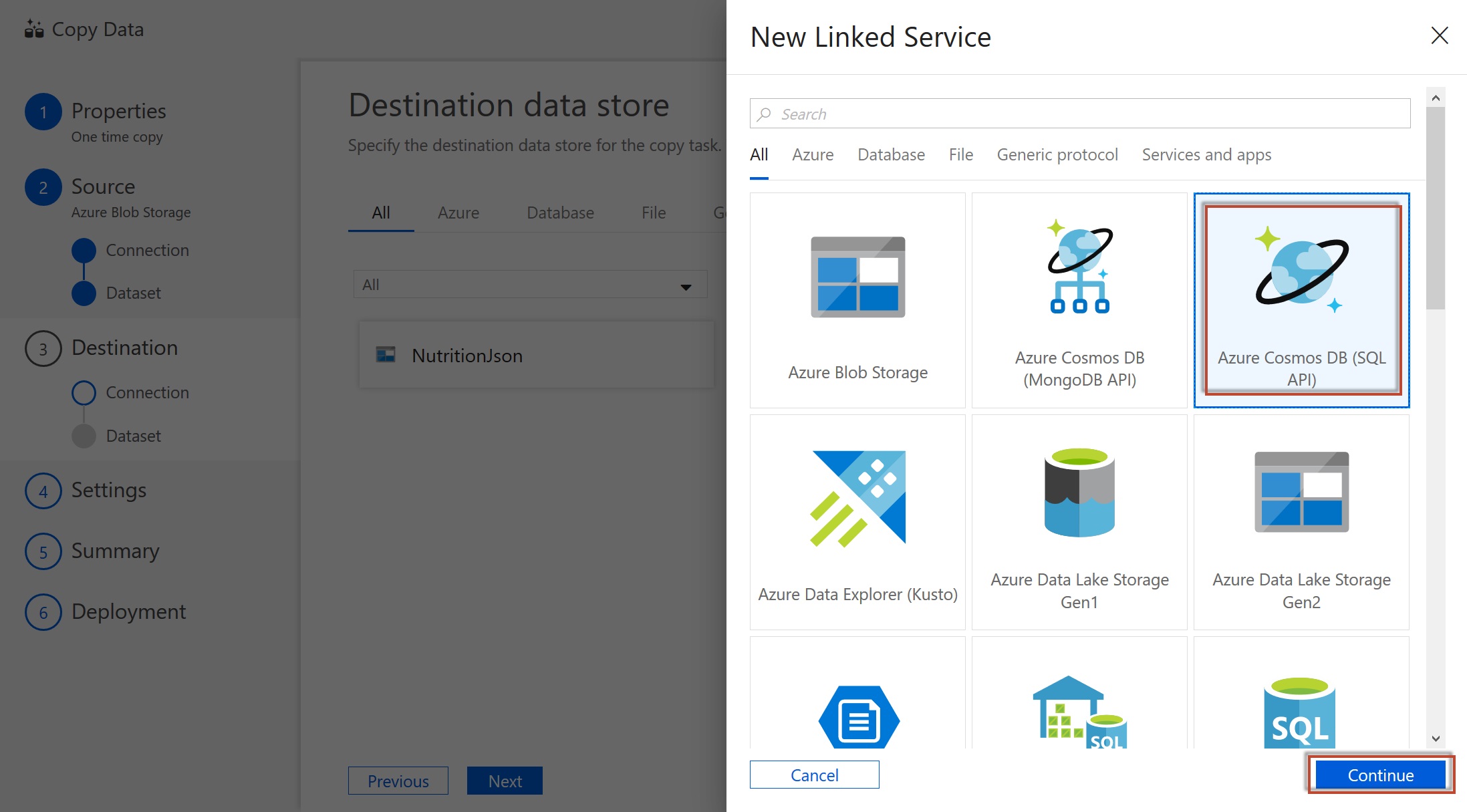
-
Name the linked service targetcosmosdb and select your Azure subscription and Cosmos DB account. You should also select the Cosmos DB ImportDatabase that you created earlier.
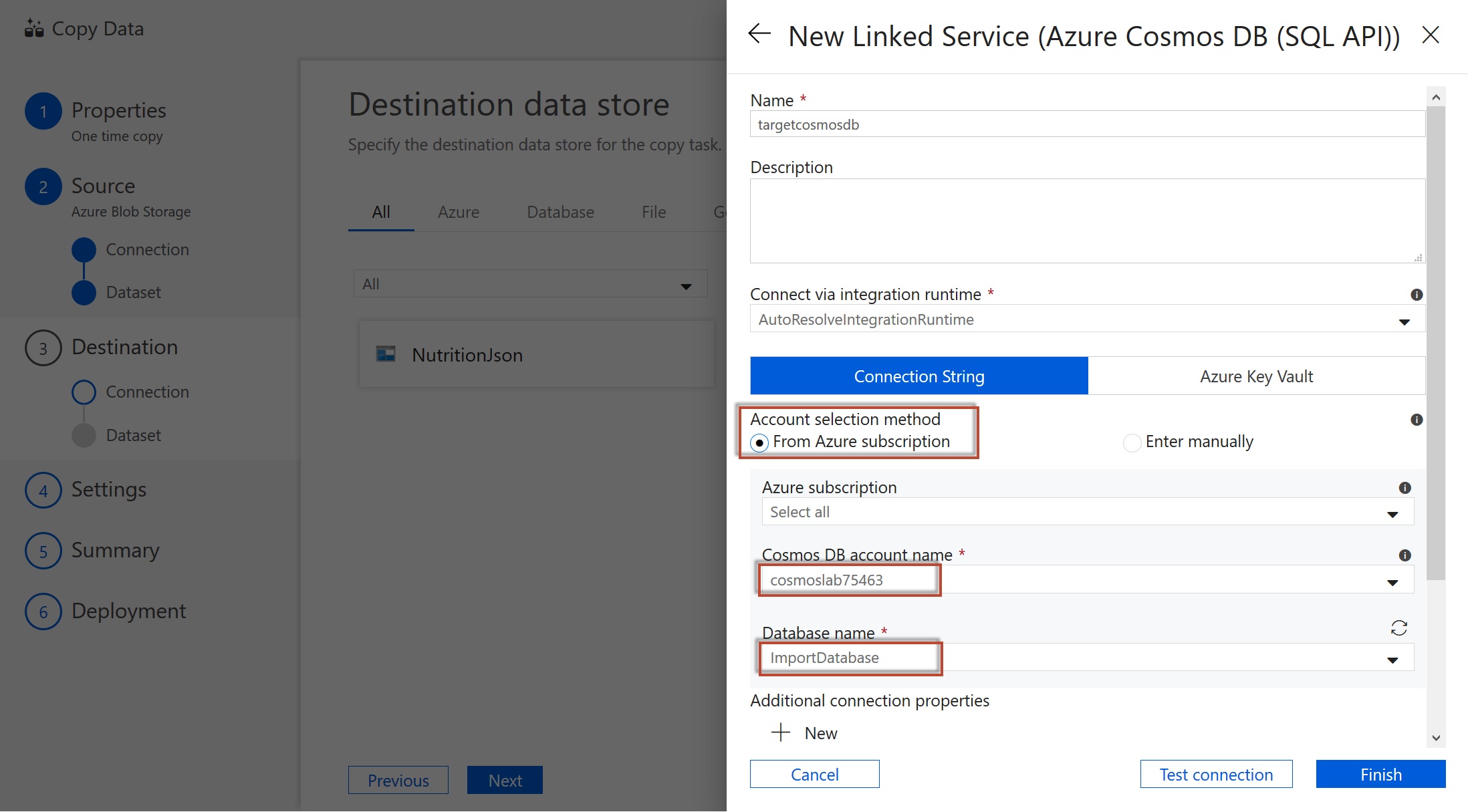
-
Select your newly created targetcosmosdb connection as the Destination data store.
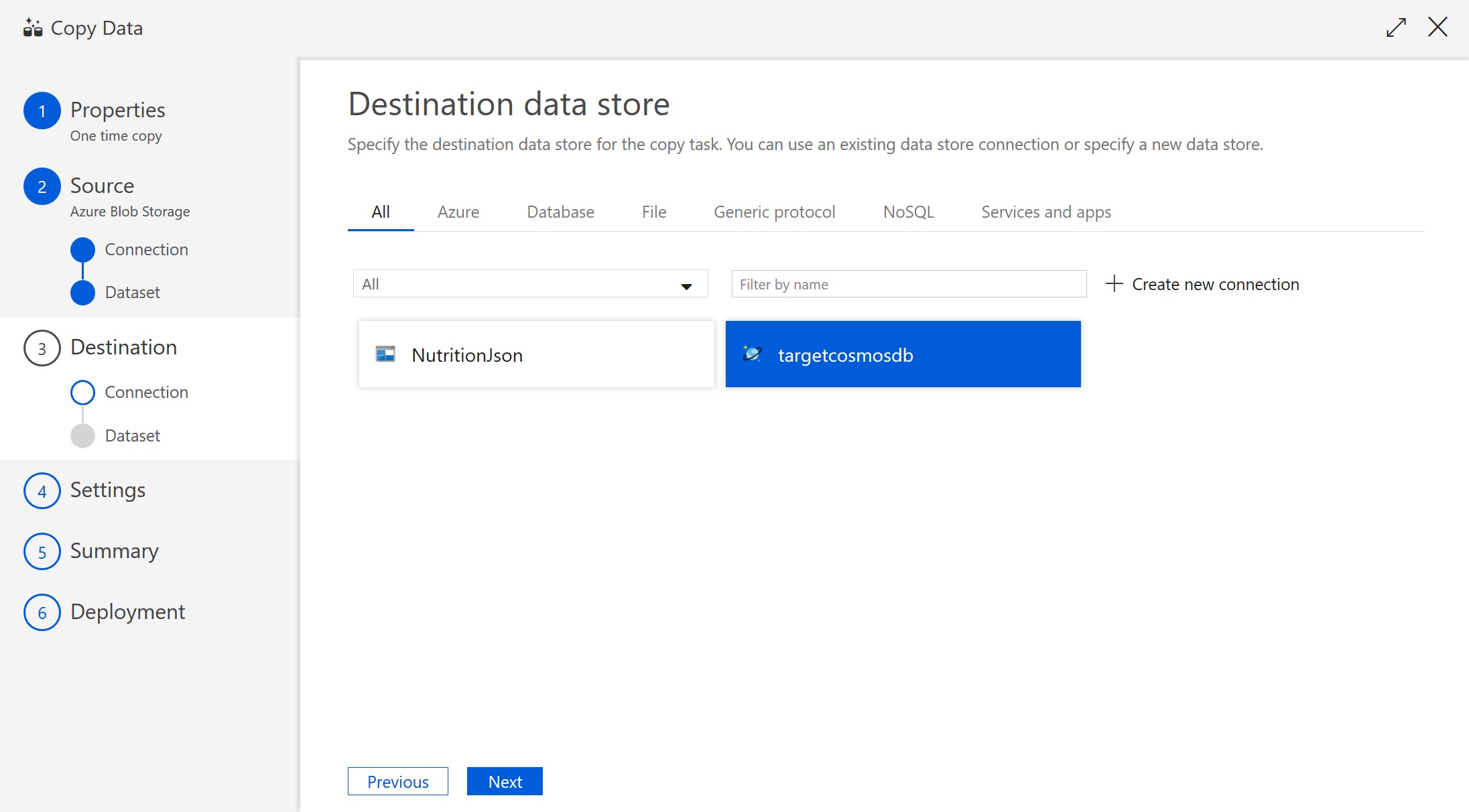
-
Select your FoodCollection container from the drop-down menu. You will map your Blob storage file to the correct Cosmos DB container. Select Next to continue.
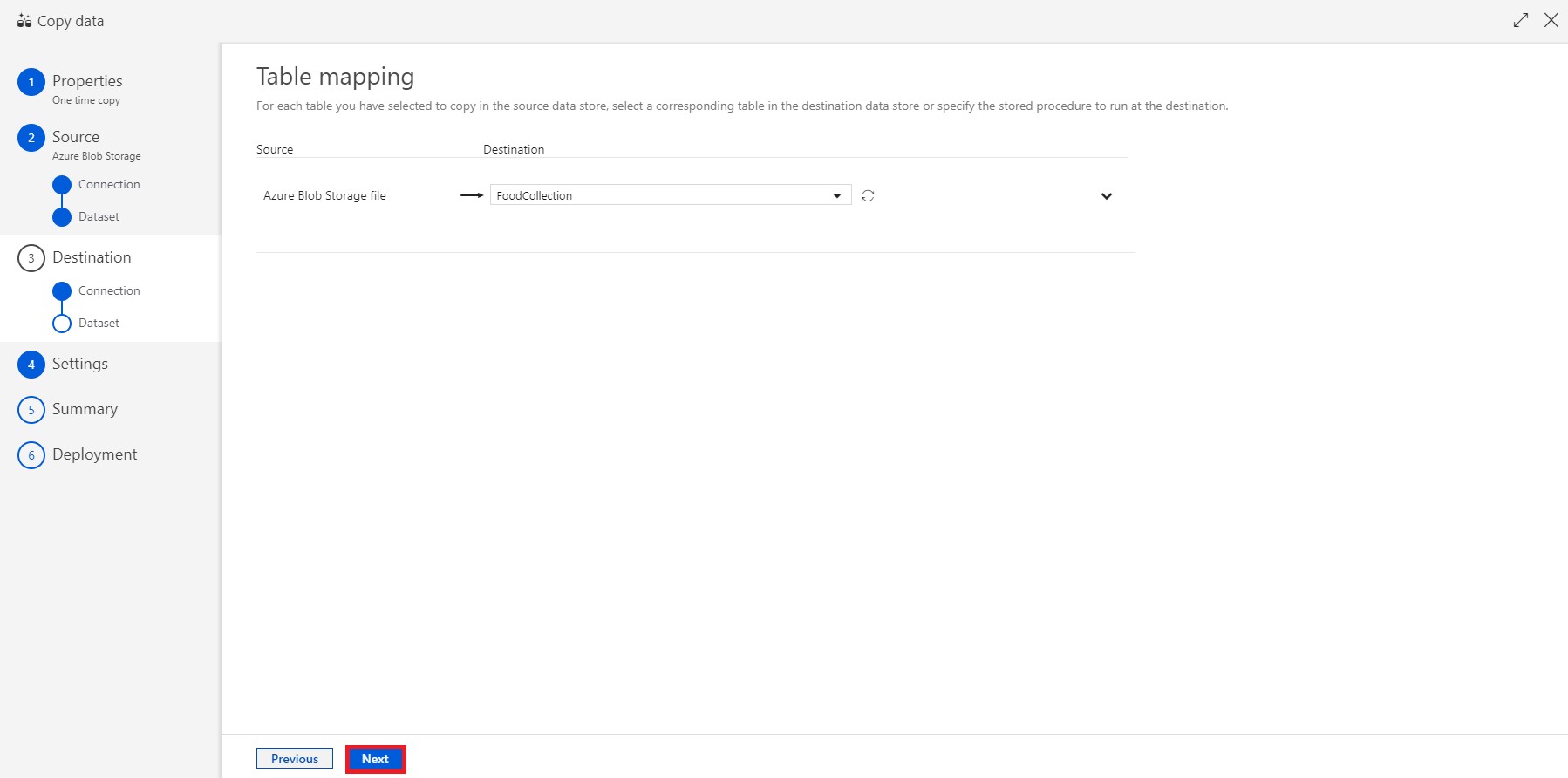
-
There is no need to change any
Settings. Select next.
-
Select Next to begin deployment After deployment is complete, select Monitor.
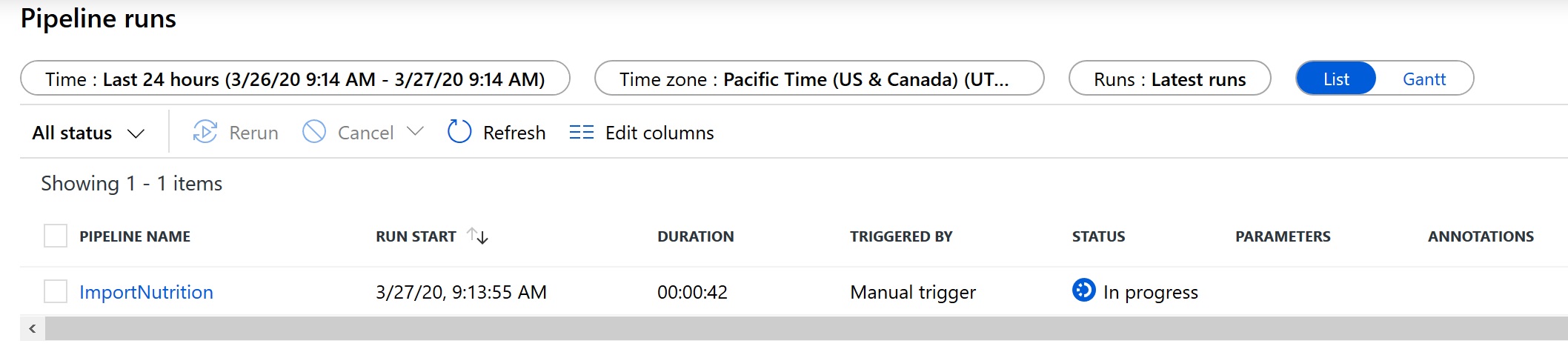
-
After a few minutes, refresh the page and the status for the ImportNutrition pipeline should be listed as Succeeded.
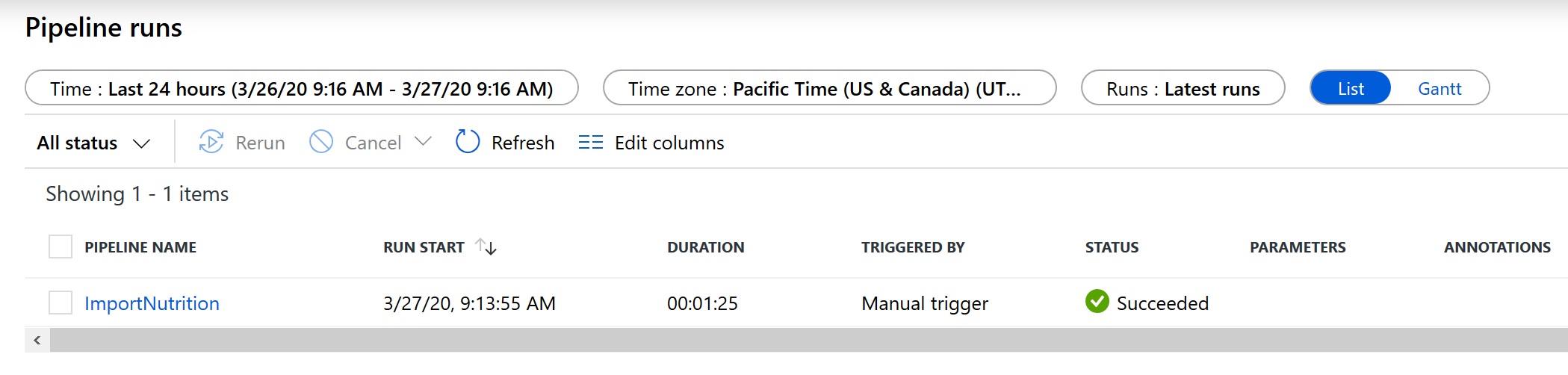
- Once the import process has completed, close the ADF. You will now proceed to validate your imported data.
Validate Imported Data
The Azure Cosmos DB Data Explorer allows you to view documents and run queries directly within the Azure Portal. In this exercise, you will use the Data Explorer to view the data stored in our container.
You will validate that the data was successfully imported into your container using the Items view in the Data Explorer.
-
Return to the Azure Portal (http://portal.azure.com).
-
On the left side of the portal, select the Resource groups link.

-
In the Resource groups blade, locate and select the cosmoslabs resource group.

-
In the cosmoslabs blade, select the Azure Cosmos DB account you recently created.

-
In the Azure Cosmos DB blade, locate and select the Data Explorer link on the left side of the blade.
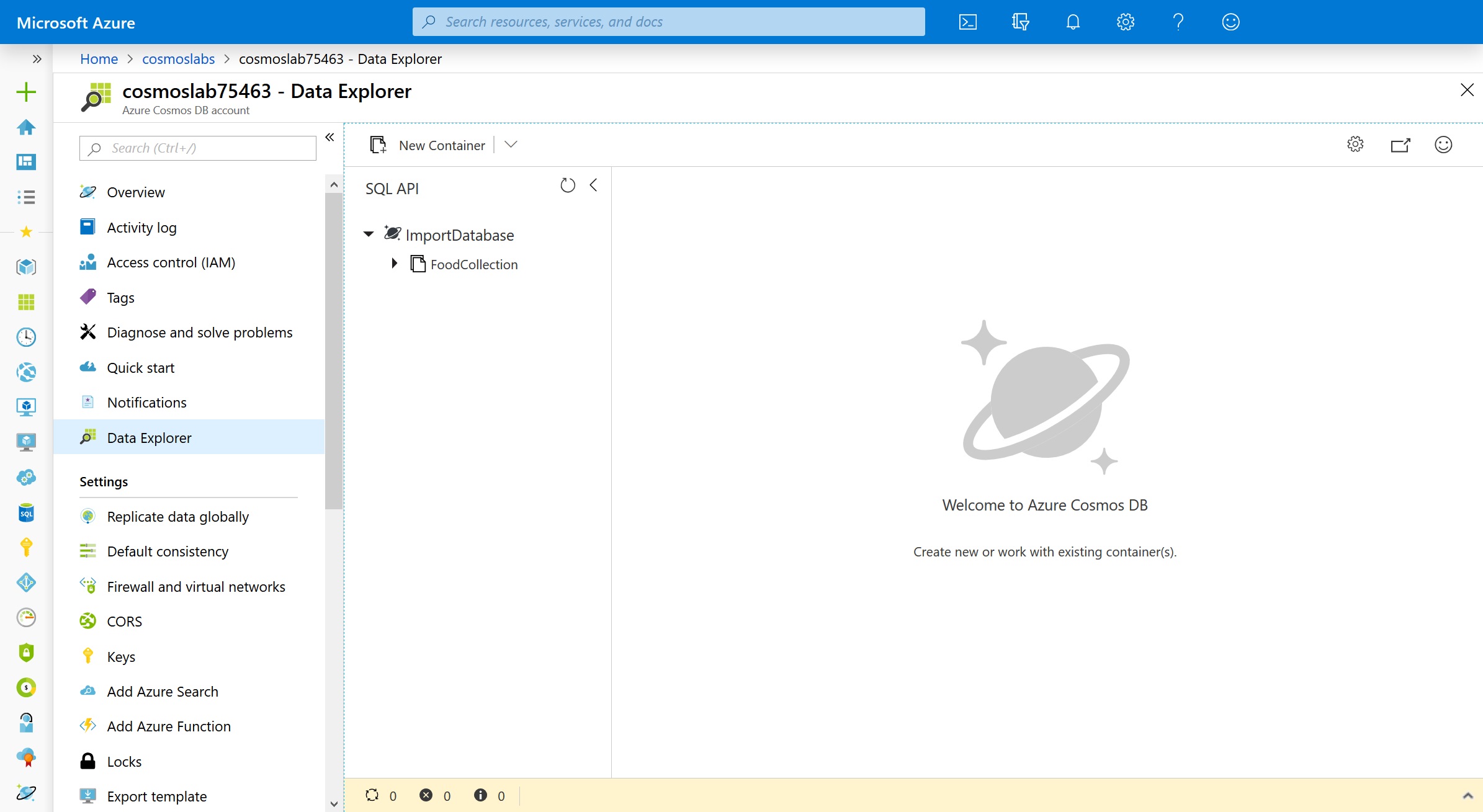
-
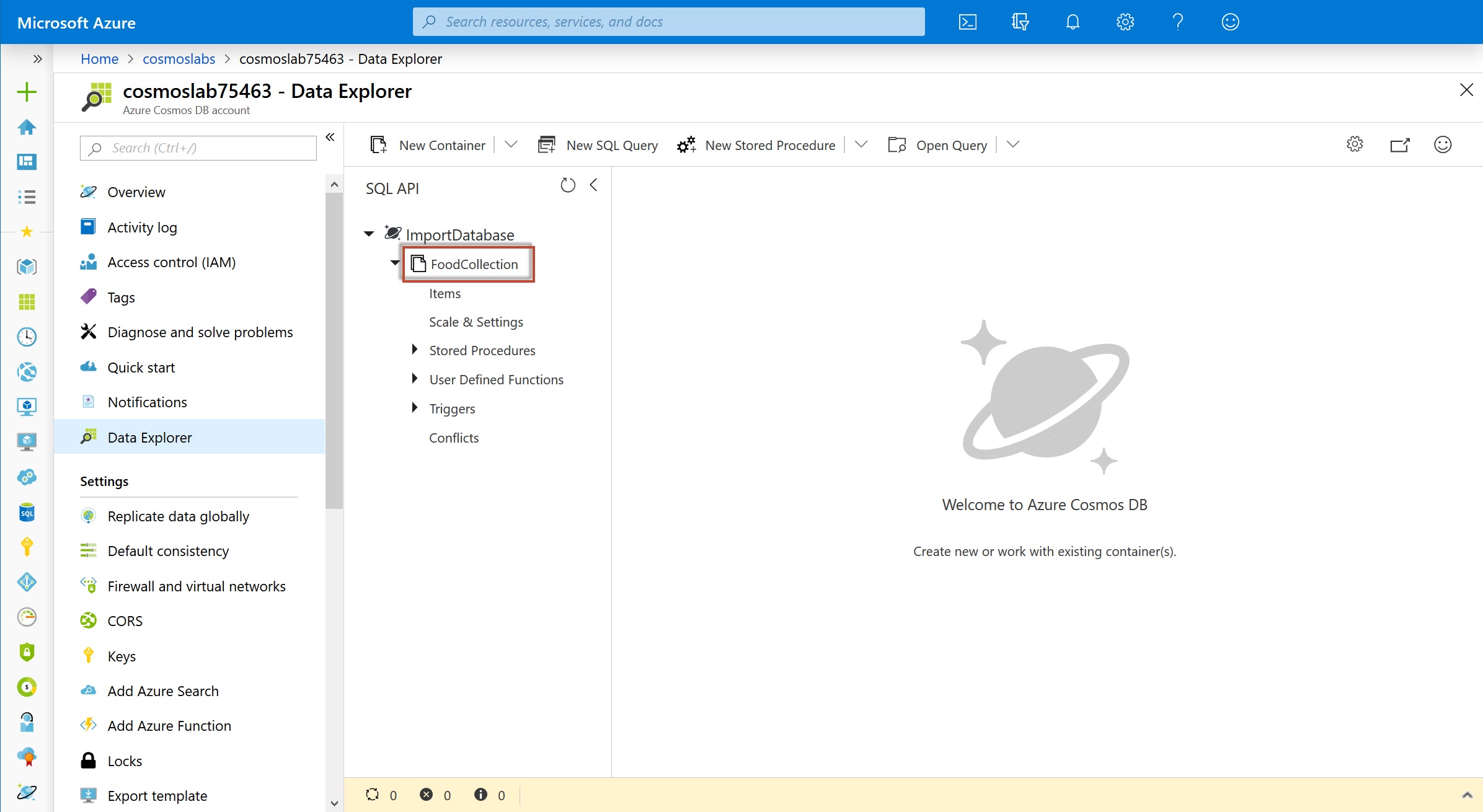
In the Data Explorer section, expand the ImportDatabase database node and then expand the FoodCollection container node.
-
Within the FoodCollection node, select the Scale and Settings link to view the throughput for the container. Reduce the throughput to 400 RU/s.
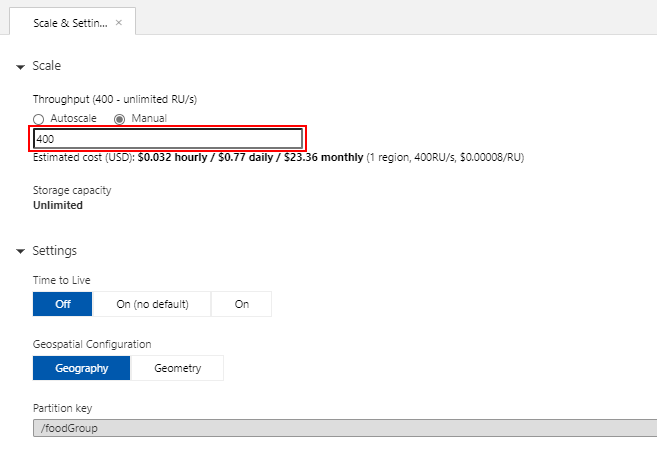
-
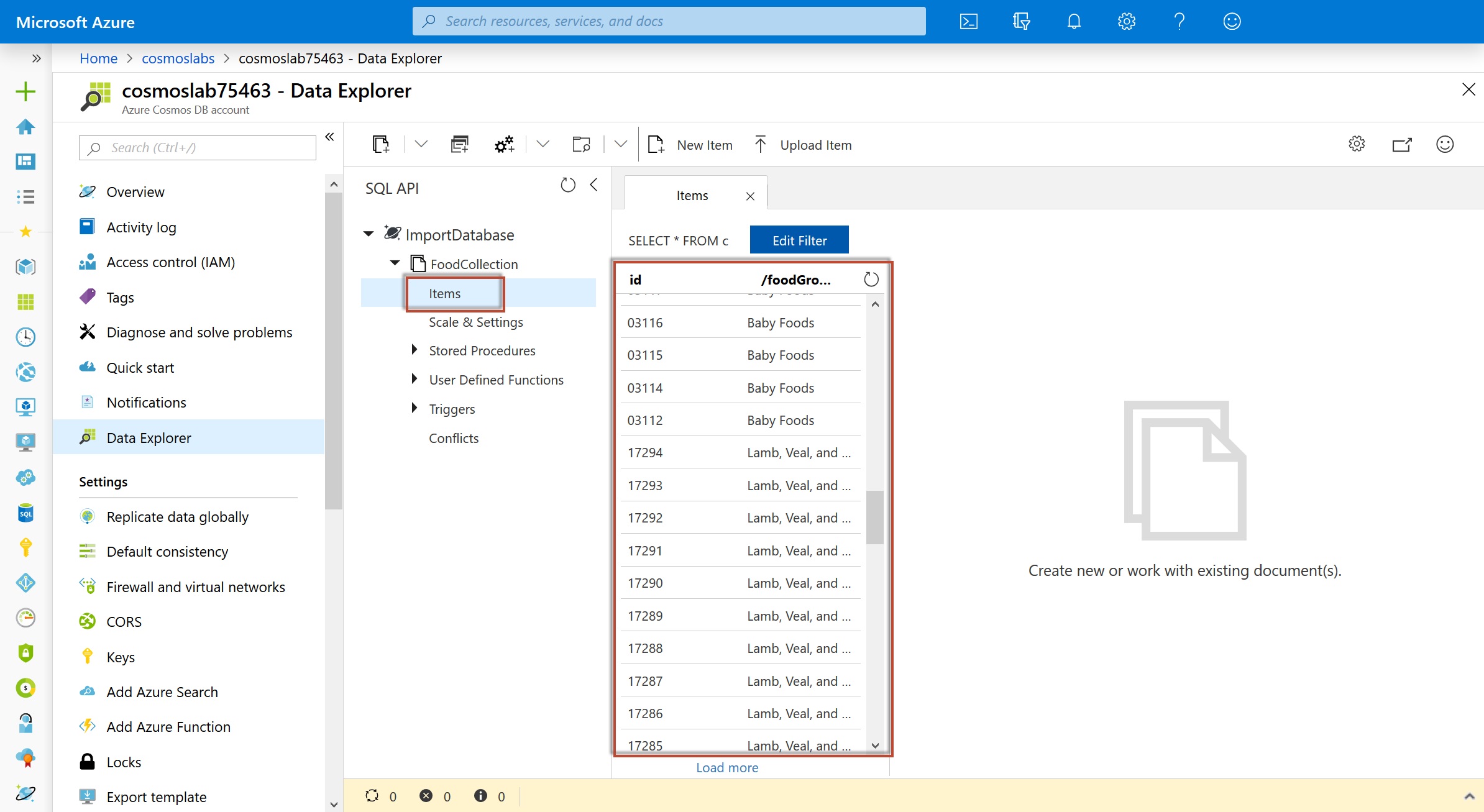
Within the FoodCollection node, select the Items link to view a subset of the various documents in the container. Select a few of the documents and observe the properties and structure of the documents.
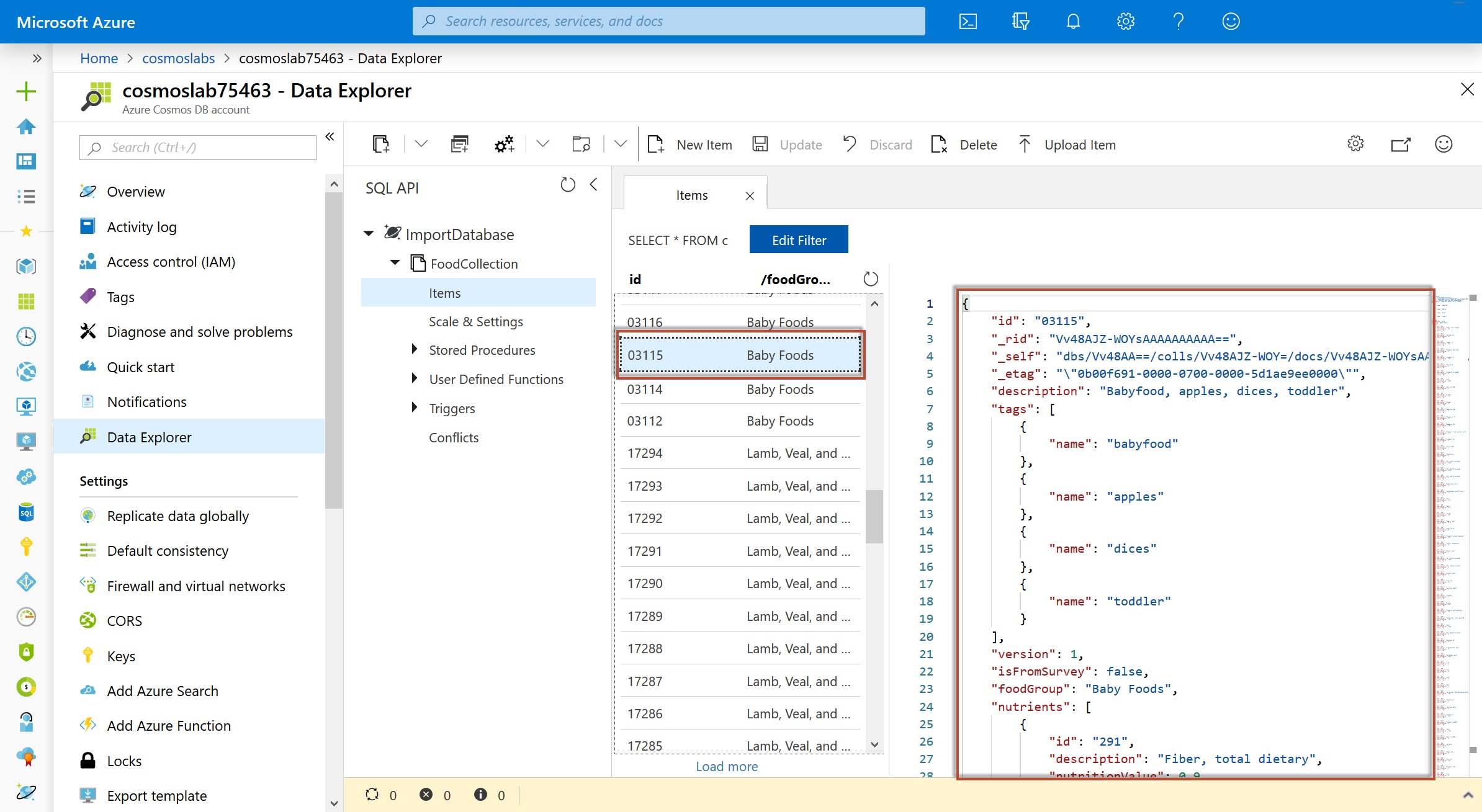
If this is your final lab, follow the steps in Removing Lab Assets to remove all lab resources.