Optimistic Concurrency Control
Viewing the ETag Property of a Requested Resource
The SQL API supports optimistic concurrency control (OCC) through HTTP entity tags, or ETags. Every SQL API resource has an ETag, and the ETag is set on the server every time an item is updated. In this exercise, we will view the ETag property of a resource that is requested using the SDK.
If this is your first lab and you have not already completed the setup for the lab content see the instructions for Account Setup before starting this lab.
Open the CosmosLabs Maven Project Template
-
Open Visual Studio Code.
-
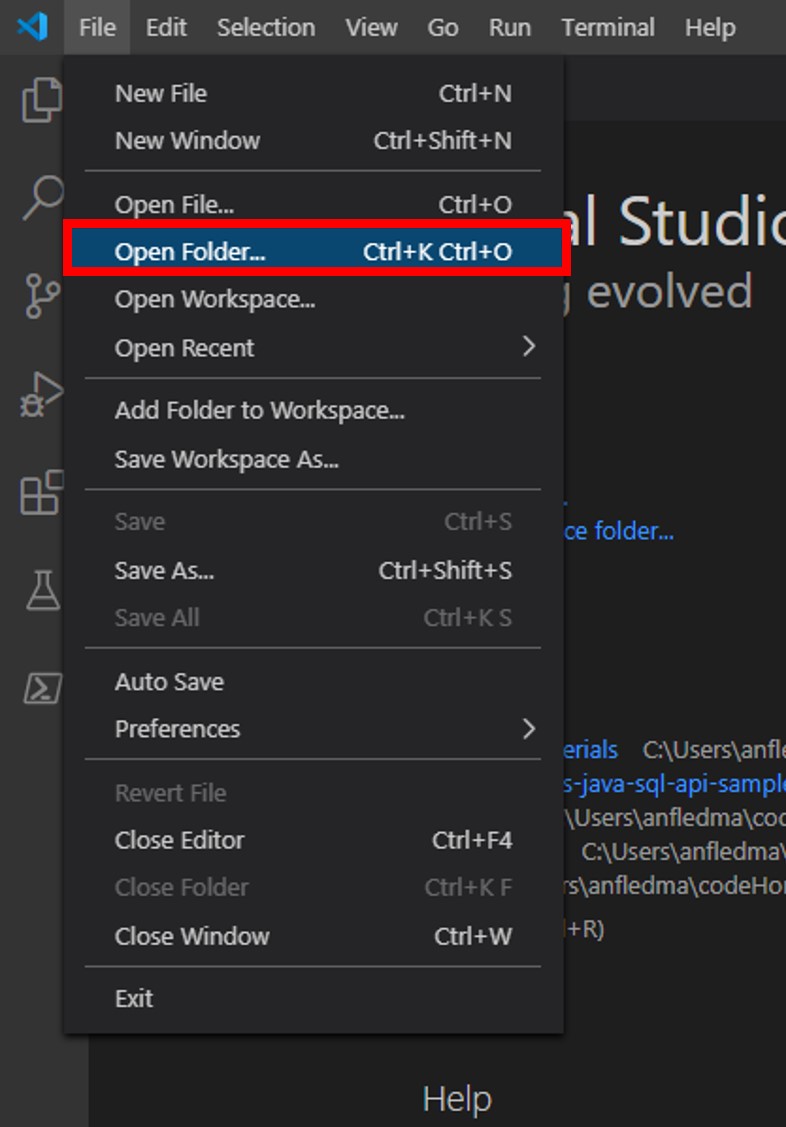
If you are completing this lab through Microsoft Hands-on Labs, the CosmosLabs folder will be located at the path: your\home\directory\Documents\CosmosLabs. In Visual Studio Code, go to File > Open Folder > to get an Open Folder dialog and and use the dialog to open the CosmosLabs folder.
-
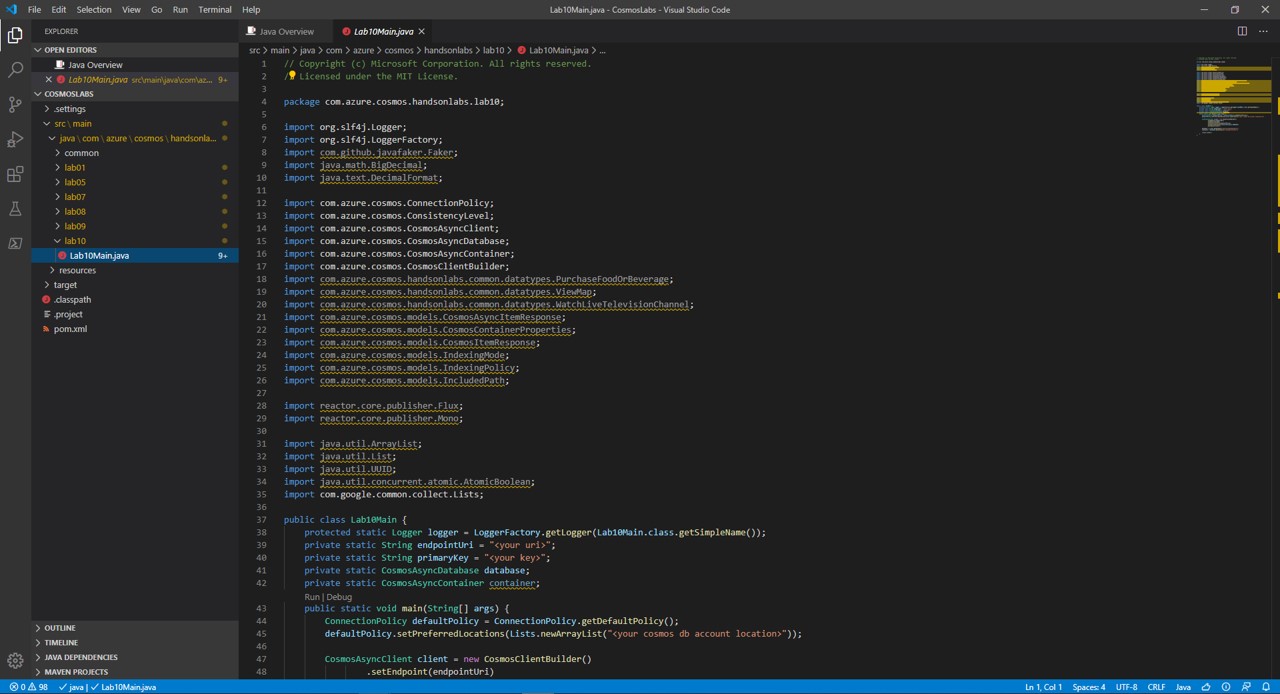
Expand the directory tree to src\main\java\com\azure\cosmos\handsonlabs\lab10\ folder. This directory is where you will develop code for this Lab. You should see only a Lab10Main.java file - this is the main class for the project.
-
Open Lab10Main.java in the editor by clicking on it in the Explorer pane.
-
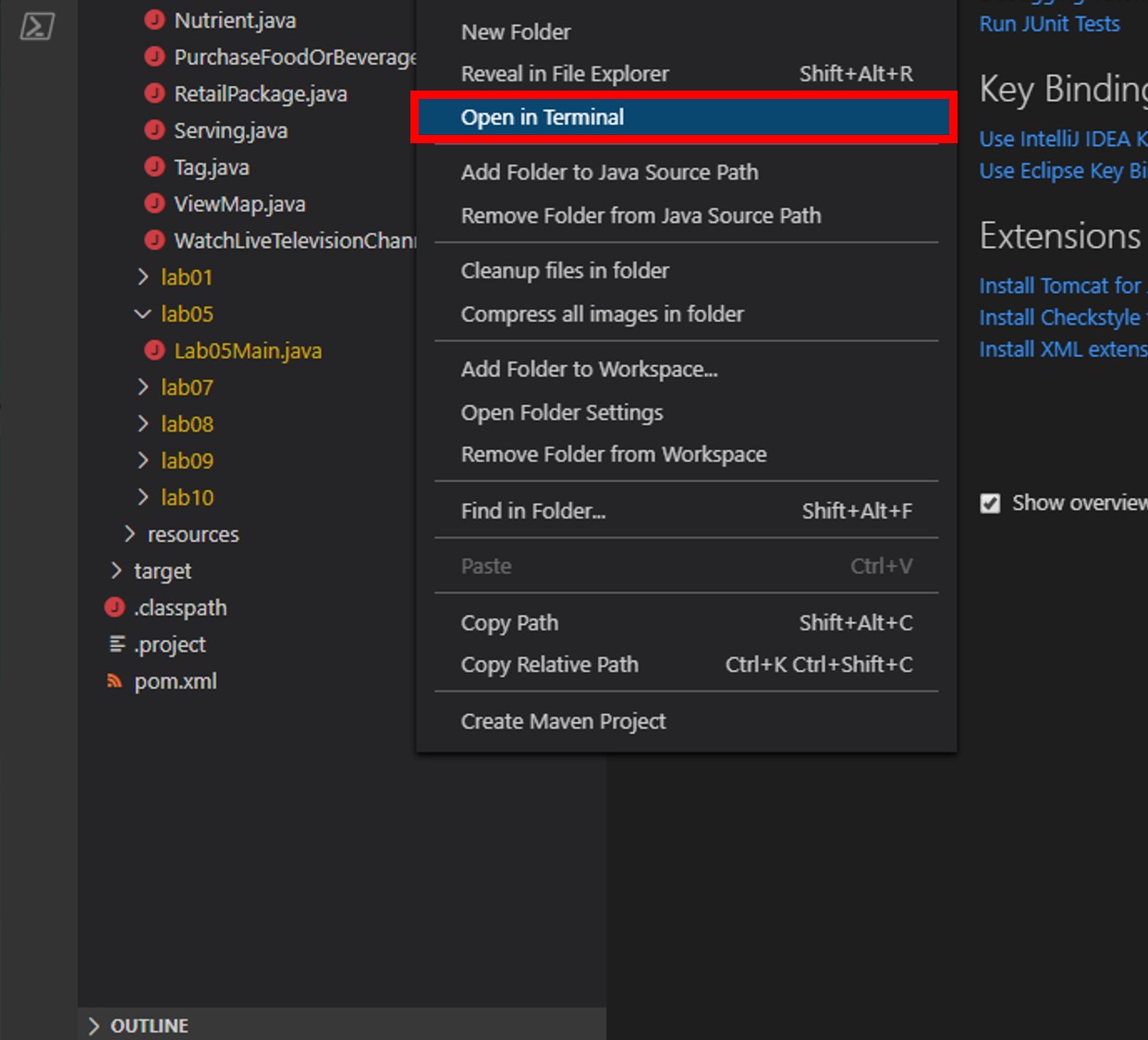
In the Visual Studio Code window, in the Explorer pane, right-click the empty space in pane and choose the Open in Terminal menu option.
-
Let’s start by building the template code. In the open terminal pane, enter and execute the following command:
mvn clean packageThis command will build the console project.
-
Click the 🗙 symbol to close the terminal pane.
-
For the
endpointUrivariable, replace the placeholder value with the URI value and for theprimaryKeyvariable, replace the placeholder value with the PRIMARY KEY value from your Azure Cosmos DB account. Use these instructions to get these values if you do not already have them:For example, if your uri is
https://cosmosacct.documents.azure.com:443/, your new variable assignment will look like this:private static String endpointUri = "https://cosmosacct.documents.azure.com:443/";.For example, if your primary key is
elzirrKCnXlacvh1CRAnQdYVbVLspmYHQyYrhx0PltHi8wn5lHVHFnd1Xm3ad5cn4TUcH4U0MSeHsVykkFPHpQ==, your new variable assignment will look like this:private static String primaryKey = "elzirrKCnXlacvh1CRAnQdYVbVLspmYHQyYrhx0PltHi8wn5lHVHFnd1Xm3ad5cn4TUcH4U0MSeHsVykkFPHpQ==";.We are now going to implement a sample query to make sure our client connection code works.
Observe the ETag Property
-
Double-click the Lab10Main.java link in the Explorer pane to open the file in the editor.
-
Locate the client-create/client-close block within the main method:
CosmosAsyncClient client = new CosmosClientBuilder() .endpoint(endpointUri) .key(primaryKey) .consistencyLevel(ConsistencyLevel.EVENTUAL) .contentResponseOnWriteEnabled(true) .buildAsyncClient(); database = client.getDatabase("NutritionDatabase"); container = database.getContainer("FoodCollection"); client.close(); -
Add the following lines of async code which use the
readItemfunction to retrieve a single item from your Cosmos DB, identified by its partition key and id:container.readItem("21083", new PartitionKey("Fast Foods"), Food.class) .flatMap(fastFoodResponse -> { logger.info("Read {}",fastFoodResponse.getETag()); return Mono.empty(); }).block();This block of code includes a line which shows the current ETag value of the item.
The ETag header and the current value are included in all response messages.
-
Save all of your open editor tabs.
-
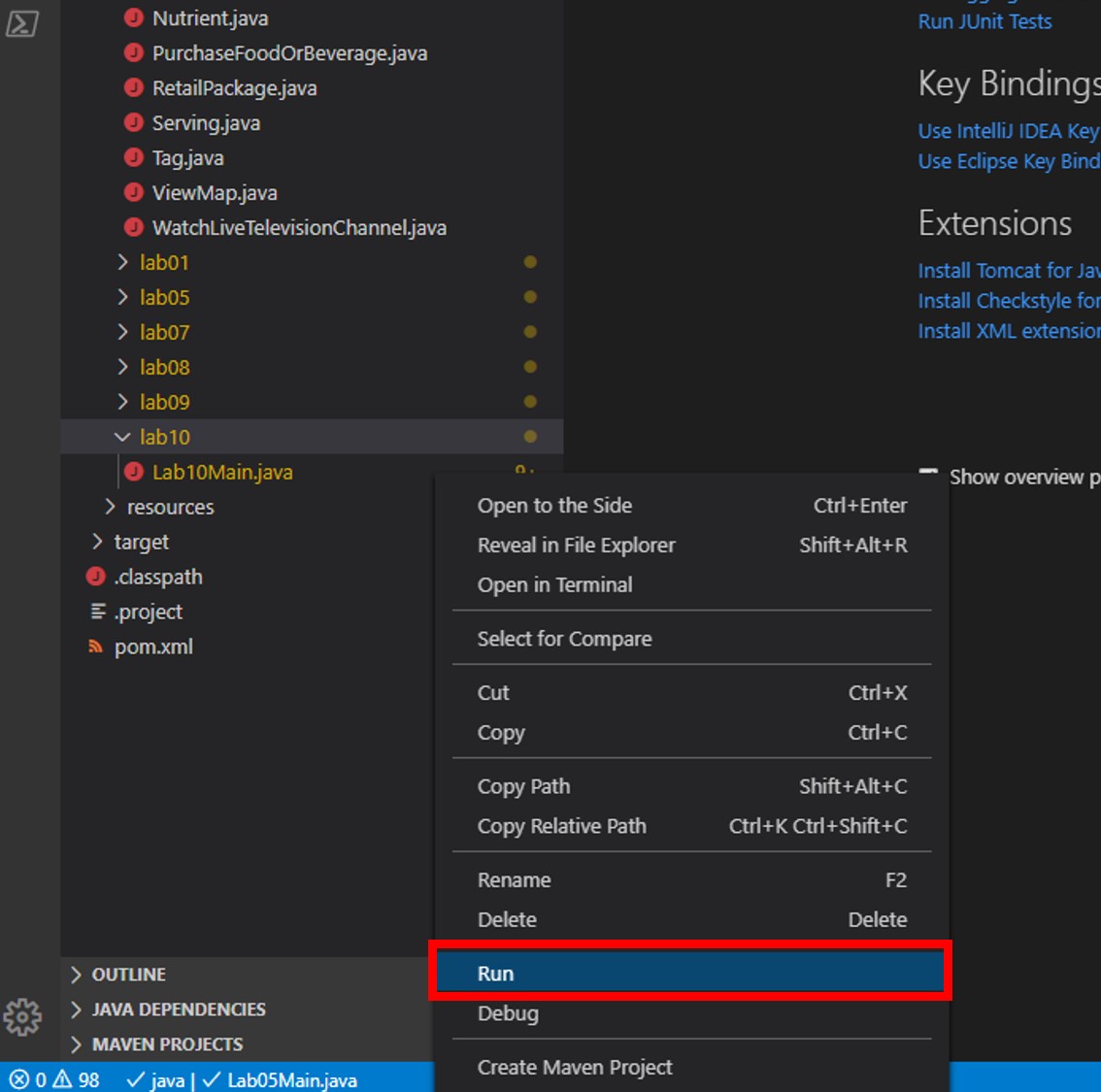
In the Explorer pane, right-click Lab10Main.java and choose the Run menu option.
This command will build and execute the console project.
-
Observe the output of the console application.
You should see an ETag for the item.
-
Following the same procedure, run Lab10Main.java again and observe the output of the console application.
The ETag should remain unchanged since the item has not been changed.
-
Click the 🗙 symbol to close the terminal pane.
-
Once again, locate the client-create/client-close block within the main method:
CosmosAsyncClient client = new CosmosClientBuilder() .endpoint(endpointUri) .key(primaryKey) .consistencyLevel(ConsistencyLevel.EVENTUAL) .contentResponseOnWriteEnabled(true) .buildAsyncClient(); database = client.getDatabase("NutritionDatabase"); container = database.getContainer("FoodCollection"); //... client.close(); -
Within the main method, locate the following line of code:
logger.info("ETag: {}",fastFoodResponse.getResponseHeaders().get("etag"));Replace that line of code with the following code:
logger.info("Existing ETag: {}",fastFoodResponse.getResponseHeaders().get("etag")); -
After the line above (and before the
returnstatement), add the code below to create aCosmosItemRequestOptionsinstance that will use the ETag from the item and specify an If-Match header:CosmosItemRequestOptions requestOptions = new CosmosItemRequestOptions(); requestOptions.setIfMatchETag(fastFoodResponse.getResponseHeaders().get("etag")); -
Add two new lines of code to retrieve the point-read item and update a property of the retrieved item:
Food fastFood = fastFoodResponse.getItem(); fastFood.addTag(new Tag("Demo"));These lines of code will modify a property of the item. Here we are modifying the tags collection property by adding a new Tag object.
-
Now add a line which invokes the async
upsertItemmethod passing in both the item and the options:CosmosItemResponse upsertResponse = container.upsertItem(fastFood,requestOptions).block(); -
Finally, add a line of code to print out the ETag of the newly updated item, as shown below:
logger.info("New ETag: {}",upsertResponse.getResponseHeaders().get("etag")); -
Your main method should now look like this:
public class Lab10Main { protected static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Lab10Main.class.getSimpleName()); private static String endpointUri = "<your uri>"; private static String primaryKey = "<your key>"; private static CosmosAsyncDatabase database; private static CosmosAsyncContainer container; public static void main(String[] args) { CosmosAsyncClient client = new CosmosClientBuilder() .endpoint(endpointUri) .key(primaryKey) .consistencyLevel(ConsistencyLevel.EVENTUAL) .contentResponseOnWriteEnabled(true) .buildAsyncClient(); database = client.getDatabase("NutritionDatabase"); container = database.getContainer("FoodCollection"); container.readItem("21083", new PartitionKey("Fast Foods"), Food.class) .flatMap(fastFoodResponse -> { logger.info("Existing ETag: {}",fastFoodResponse.getResponseHeaders().get("etag")); CosmosItemRequestOptions requestOptions = new CosmosItemRequestOptions(); requestOptions.setIfMatchETag(fastFoodResponse.getResponseHeaders().get("etag")); Food fastFood = fastFoodResponse.getItem(); fastFood.addTag(new Tag("Demo")); CosmosAsyncItemResponse<Food> upsertResponse = container.upsertItem(fastFood,requestOptions).block(); logger.info("New ETag: {}",upsertResponse.getResponseHeaders().get("etag")); return Mono.empty(); }).block(); client.close(); } } -
Save all of your open editor tabs.
-
Build and execute the console project, following the same process as you did previously.
-
Observe the output of the console application.
You should see that the value of the ETag property has changed. The CosmosItemRequestOptions class helped us implement optimistic concurrency by specifying that we wanted the SDK to use the If-Match header to allow the server to decide whether a resource should be updated. The If-Match value is the ETag value to be checked against. If the ETag value matches the server ETag value, the resource is updated. If the ETag is no longer current, the server rejects the operation with an “HTTP 412 Precondition failure” response code. The client then re-fetches the resource to acquire the current ETag value for the resource.
-
Click the 🗙 symbol to close the terminal pane.
-
Add two new lines of code to again update a property of the item:
fastFood = upsertResponse.getItem(); fastFood.addTag(new Tag("Failure")); -
Add a new line of code to again invoke the
upsertItemmethod passing in both the updated item and the same options as before:upsertResponse = container.upsertItem(fastFood,requestOptions).block();The
CosmosItemRequestOptionsinstance has not been updated, so is still using the ETag value from the original object, which is now out of date so we should expect to get an error. -
Add error handling to the
upsertItemcall you just added by wrapping it with a try-catch and then output the resulting error message. The code should now look like this:try { upsertResponse = container.upsertItem(fastFood,requestOptions).block(); } catch (Exception ex) { logger.error("Update error",ex); } -
Save all of your open editor tabs.
-
Build and execute the project as you have in previous steps.
-
Observe the output of the console application.
You should see that the second update call fails because value of the ETag property has changed. The
CosmosItemRequestOptionsclass specifying the original ETag value as an If-Match header caused the server to decide to reject the update operation with an “HTTP 412 Precondition failure” response code. -
Click the 🗙 symbol to close the terminal pane.
-
Close all open editor tabs.
-
Close the Visual Studio Code application.